THE dreaded TEST CROSS
Determining the phenotype of an organism is fairly straight forward ... you look at it (since phenotype means physical characteristics).
Determining genotype isn't as cut & dry because you can't see an organism's genes by just looking at it.Before we dive into the TEST CROSS, let's review our three possible genotypes & the phenotypes they create. For our example let's use guinea pig fur color; black being dominant (B) & white being recessive (b).
|
NAME |
ABBREVIATION |
ORGANISM |
|
(Pure Dominant) |
|
|
|
(Hybrid) |
|
|
|
(Pure Recessive) |
|
|
|
|
Notice how easy it is to determine the phenotype of a guinea pig. You look at it. You see either black or white fur. Whichever color you see is the pig's phenotype with respect to the fur color trait. Easy as pie.Notice also that the only genotype that produces the recessive trait is homozygous recessive ("bb" in our example). So if an organism shows a recessive trait in its phenotype, its genotype must be homozygous recessive.
Examples:If we see a white guinea pig, it's genotype must be "bb". If you look at a pea plant & it is short, its genotype must be "tt". You bump into a two-eyed purple people eater on your way to the mall, its genotype for eyes is "ee", because we all know that in purple people eaters the dominant trait is one eye (EE or Ee).
So remember,
AN ORGANISM WITH A RECESSIVE TRAIT ALWAYS HAS A HOMOZYGOUS RECESSIVE GENOTYPE (two lowercase letters).
|
|
If I handed you a black guinea pig & asked,"What's its phenotype for fur color?" You would gently hold the guinea pig, look at it and reply, "Black, you dummy ... all you gotta do is look at it". And I would say, "Correct, & please don't call me dummy".Our black guinea pig is either BB or Bb, which one is it?If I handed you the same guinea pig & asked, "What's the genotype of this guinea pig with respect to its fur color?" You wouldn't be able to tell me, and I wouldn't be able to tell you either. The reason we don't know is because there are two genotypes that BOTH produce a dominant trait phenotype, homozygous dominant (BB) & heterozygous (Bb), & we can't see the actual alleles (letters) without serious scientific chromosomal-type analysis --- and that's assuming that a Guinea Pig Genome Project has been completed for us to refer to, & I don't think it has.
(How is that for a really bad run-on sentence? My apologies to English teachers everywhere.)
So how do we figure it out? We perform a TEST CROSS !Now, I must tell you that in your life, as an exceptional biology student, you will most likely NEVER actually PERFORM a test cross. What you need to understand are the possible results of a test cross & what they mean.Test cross = the cross of an organism with an unknown dominant genotype with an organism that is homozygous recessive for that trait
|
THE GENOTYPE OF THE PARENT WITH THE DOMINANT TRAIT MUST BE HETEROZYGOUS. |
In our scenario, if we see any white baby guinea piglets, our black parent pig is "Bb". If all the baby piglets are black, the black parent is "BB".
I should mention that the reliability of a test cross increases with the number of offspring produced. So ideally (in our example) we would want a large litter of guinea pigs to look at. If a small litter is produced (like only 4 or 5 or 6), we would probably have those same parent guinea pigs "do it" again & make more offspring so that our conclusion is more reliable.
| To summarize a little, here are the "Key
Points" to remember about a TEST CROSS.
1. the organism with the dominant trait is always crossed with an
organism with the recessive trait
|
That's the bottom-line on a test cross, that stuff in the table. But you don't want to settle for just the bottom line. You want to understand the concept in a little more detail, don't you? Yes, believe me, you do.
In our guinea pig example, our mystery black pig is either BB or
Bb. Allow me to use "B?" for the mystery genotype. Thanks.
The white guinea pig is "bb" because white is the recessive trait
& the only way a recessive trait appears is if the genotype is homozygous
recessive. Let's put this info in a series of Punnett Squares.
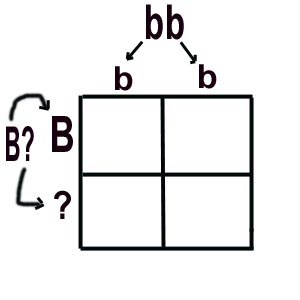 |
Our black guinea pig parent is on the left, and the white parent
is up above.
Notice that the offspring will inherit only "b's" from the white parent. Let's fill-in the boxes with all the alleles that we KNOW ... |
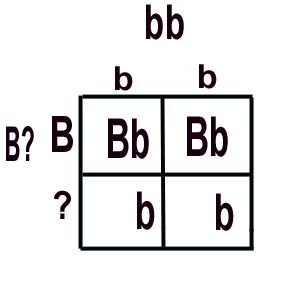 |
The hybrid ("Bb") baby guinea pigs across the top will be black.
For the offspring in that bottom row, their phenotype depends on what that second ("?") allele is in our black guinea pig parent. There are two possibilities ... |
Possibility #1:
Black Parent is BB 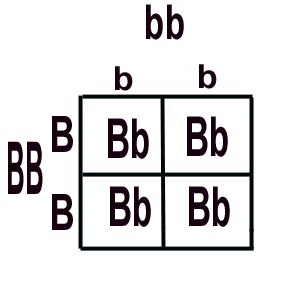
OR Possibility #2: Black Parent is Bb 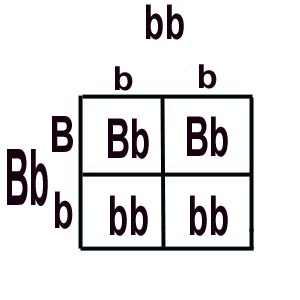
|
As you can see, if our mystery genotype pig has a "B" in the "?" spot, all of the offspring from the test cross will be heterozygous (Bb) & have the dominant phenotype --- black fur. There is NO WAY white guinea pigs can be produced because to be white
the offspring need to inherit one little "b" from each parent, and
in this scenario the black parent doesn't have ANY little "b's" to pass
on.
On the other hand, if the mystery allele "?" = "b", then we can predict that half (2 of 4 boxes) of the offspring from the test cross are going to have the recessive phenotype; i.e. have white fur. The only way to get white guinea pig piglets is if both parent guinea pigs have at least one "b". We KNOW the white parent has got 'em (the only way to be white is to be "bb"), and we KNOW the black parent has one big "B" (has to in order to be black), so if we get white offspring, that second allele in the black parent is "b". Think of it this way: Our test cross = mystery black genotype x recessive white genotype = B__ x bbSo if any recessive offspring are produced, the dominant parent is hybrid (heterozygous). |
| Here are those "KEY POINTS" one
more time:
In a TEST CROSS, 1. the organism with the dominant trait is always crossed with an organism with the recessive trait 2. if ANY offspring show the recessive trait, the unknown genotype is heterozygous 3. if ALL the offspring have the dominant trait, the unknown genotype is homozygous dominant 4. large numbers of offspring are needed for reliable results |
1. In African-violet plants, purple flowers are dominant to white flowers. You purchase an African-violet plant with white flowers. It's genotype could be represented as :
A. PP2. To discover whether an animal showing the dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous, it must be crossed with an animal that is:
B. Pp
C. pP
D. pp
A. homozygous dominant3. Two tall pea plants are crossed, producing 105 tall plants & 32 short plants. The genotypes of the tall parent plants are:
B. homozygous recessive
C. heterozygous
D. choices B & C
A. Tt & Tt4. A spotted dalmation is mated with a pure-white dalmation (ss) to deteremine whether its genotype is SS or Ss for spots. Three puppies are born, all with spots. We can conclude that the spotted dalmation is SS.
B. TT & Tt
C. Tt & tt
D. tt & tt
A. true5. In mice brown (B) is dominant to white (b). A brown mouse is mated with a white mouse. Twelve brown mice are produced. The brown mouse's genotype is:
B. false
A. BB6. Two brown-eyed parents have a child with blue eyes. The best explanation is:
B. Bb
C. bb
D. a reliable conclusion can't be reached
A. a mutation occured before the child was born7. Which scenario best supports the conclusion that a black guinea pig's genotype is homozygous dominant?
B. both parents carry the allele for blue eyes
C. both parents are pure for brown eyes
D. they wore blue contacts during sexual intercourse
A. after mating with a white guinea pig, 2 black & 2 white guinea pigs were produced8. Individuals with the same phenotype have the same genotype.
B. after mating with a white guinea pig, 10 black & 8 white guinea pigs were produced
C. after mating with a white guinea pig, 12 black guinea pigs were produced
D. after mating with a black guinea pig, 4 black guinea pigs were produced
A. true9. In a test cross to determine whether a fruit fly is homozygous (WW) or heterozygous (Ww) for long wings, 7 long-winged flies & 1 short winged-fly are produced. Which is a valid conclusion?
B. false
A. the unknown fruit fly is WW10. In hamsters, long tails (L) are dominant to short tails (l). A student wishes to perform a test cross to determine whether a female long-tailed hamster is homozygous or heterozygous for long tail length. She mates the hamster with a male long-tailed hamster & studies the offspring, which are 100% long-tailed. She conclude that the female hamster's genotype is "LL". What mistake(s) did the student make?
B. the unknown fruit fly is Ww
C. the unknown fruit fly is ww
D. more offspring are needed
A. she should have mated the female hamster with a male that was known to be hybrid
B. she should have mated the female hamster with a short-tailed male hamster
C. she should have mated the female hamster with another long-tailed female
D. she has to mate memers of the litter before she can make a conclusion
| <cLiCK hErE for AnSWErs> |
Like I stated ealier, it is highly unlikely that you will be asked to actually perform a test cross --- like really mate two organisms & then analyze their offspring. If you do, consider yourself lucky & more power to ya. Perhaps you'll be fortunate enough to run some computer simulations or something in lab. Anyway, the concepts behind a TEST CROSS are important. So study-up, do your best.
Later,
Waterman
1. In African-violet plants, purple flowers are dominant to white flowers. You purchase an African-violet plant with white flowers. It's genotype could be represented as :
A. PP2. To discover whether an animal showing the dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous, it must be crossed with an animal that is:
B. Pp
C. pP - (this is the same thing as choice "B")
D. pp - ORGANISMS WITH RECESSIVE TRAITS MUST BE HOMOZYGOUS RECESSIVE (2 lowercase letters)
A. homozygous dominant3. Two tall pea plants are crossed, producing 105 tall plants & 32 short plants. The genotypes of the tall parent plants are:
B. homozygous recessive - RULE #1 FOR A TEST CROSS
C. heterozygous
D. choices B & C
A. Tt & Tt - BOTH PARENT ORGANISMS MUST CARRY ONE RECESSIVE ALLELE IN ORDER TO PRODUCE RECESSIVE ORGANISMS4. A spotted dalmation is mated with a pure-white dalmation (ss) to deteremine whether its genotype is SS or Ss for spots. Three puppies are born, all with spots. We can conclude that the spotted dalmation is SS.
B. TT & Tt - (no short plants would be produced from this cross)
C. Tt & tt - (the "tt" parent would be short, the questions says both parents are tall --- can't be an answer)
D. tt & tt - (both parents were tall, can't be an answer)
A. true5. In mice brown (B) is dominant to white (b). A brown mouse is mated with a white mouse. Twelve brown mice are produced. The brown mouse's genotype is:
B. false - 3 PUPPIES IS NOT REALLY A LARGE ENOUGH NUMBER OF OFFSPRING TO BE 100% CERTAIN THAT THE DALMATION IS "DD"
A. BB - ALL DOMINANT OFFSPRING INDICATE THAT THE UNKNOWN GENOTYPE IS HOMOZYGOUS DOMINANT, 12 IS A LARGE ENOUGH LITTER6. Two brown-eyed parents have a child with blue eyes. The best explanation is:
B. Bb - (this would produce some white mice)
C. bb - ("bb" would make the brown mouse white, can't be an answer)
D. a reliable conclusion can't be reached
A. a mutation occured before the child was born7. Which scenario best supports the conclusion that a black guinea pig's genotype is homozygous dominant?
B. both parents carry the allele for blue eyes
C. both parents are pure for brown eyes
D. they wore blue contacts during sexual intercourse - (that's just silly)
A. after mating with a white guinea pig, 2 black & 2 white guinea pigs were produced - (recessive offspring would mean the parent is hybrid)8. Individuals with the same phenotype have the same genotype.
B. after mating with a white guinea pig, 10 black & 8 white guinea pigs were produced - (recessive offspring would mean the parent is hybrid)
C. after mating with a white guinea pig, 12 black guinea pigs were produced
D. after mating with a black guinea pig, 4 black guinea pigs were produced - (a correct test cross would be with a white guinea pig)
A. true9. In a test cross to determine whether a fruit fly is homozygous (WW) or heterozygous (Ww) for long wings, 7 long-winged flies & 1 short winged-fly are produced. Which is a valid conclusion?
B. false - AN ORGANISM WITH A DOMINANT PHENOTYPE CAN BE EITHER HOMOZYGOUS DOMINANT OR HETEROZYGOUS FOR THAT TRAIT
A. the unknown fruit fly is WW10. In hamsters, long tails (L) are dominant to short tails (l). A student wishes to perform a test cross to determine whether a female long-tailed hamster is homozygous or heterozygous for tail length. She mates the hamster with a male long-tailed hamster & studies the offspring, which are 100% long-tailed. She concludes that the female hamster's genotype is "LL". What mistake(s) did the student make?
B. the unknown fruit fly is Ww - THE APPEARANCE OF ANY OFFSPRING WITH THE RECESSIVE TRAIT INDICATES THAT THE UNKNOWN GENOTYPE IS HYBRID
C. the unknown fruit fly is ww
D. more offspring are needed
A. she should have mated the female hamster with a male that was known to be hybrid<BACK TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
B. she should have mated the female hamster with a short-tailed male hamster - A TEST CROSS ALWAYS INVOLVES CROSSING WITH AN ORGANISM THAT HAS THE RECESSIVE PHENOTYPE
C. she should have mated the female hamster with another long-tailed female
D. she has to mate members of the litter before she can make a conclusion